Description
Crop (Chestnuts) suitability information includes:
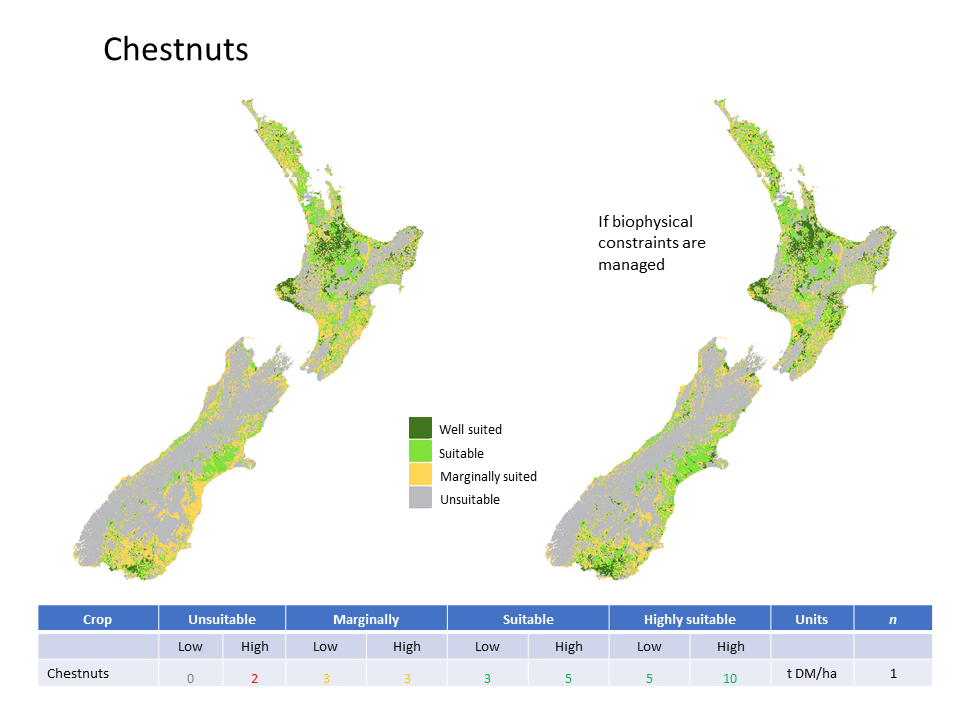
- map of suitability categories (1 - Well suited, 2 - Suitable, 3 - Marginally Suited, 4 - Unsuitable)
- rules used to generate the suitability maps
- map of suitability categories where biophysical constraints are managed through irrigation, artificial drainage, or liming
- map of the potential yield (provided as a lower/upper range)
- map of the potential yield where biophysical constraints are managed through irrigation, artificial drainage, or liming (provided as a lower/upper range)
Date: December 2023 Version: v2
Owner: MPI, Plant & Food Research, Manaaki Whenua - Landcare Research, NIWA
Contact: Dr Steve Thomas, Plant and Food Research
Our Environment
You can view the data in this dataset on a map-based web app here:
Chestnuts Suitability Categories
Preview Image
Dataset attributes
| Spatial extent |
New Zealand |
|---|
| Spatial resolution |
500 m pixel size. Resolution is based on the NIWA Virtual Climate Station Network 5km climate grid, and S-map / FSL sampled on a 500 x500 m grid |
|---|
| Temporal extent |
30 year average, climate data 1971-2000 |
|---|
| Temporal resolution |
Yield values are mean annual estimates |
|---|
| Evaluation method (Validation) |
Expert assessed |
|---|
| Evaluation result (Numeric) |
N/A |
|---|
| Evaluation result (Categorical) |
N/A |
|---|
| Uncertainty method |
None
|
|---|
| Uncertainty data format (Numeric) |
Yield information: provided as a range (low - upper each provided as a raster layer) |
|---|
| Uncertainty data format (Categorical) |
Suitability: Moderate reliability at national scale (there is a reasonable understanding of crop requirements but key inputs have limited accuracy) |
|---|
Methodology
The land suitability concept is used to characterise the degree of fitness of a given environment for specific agricultural activities. The key principle in the method is that land suitability for the growth of different plant species can be estimated from geo-referenced information on climate (e.g. temperature and rainfall regimes), soil (e.g. soil depth and pH) and terrain conditions (e.g. slope and aspect). The suitability model utilises a wider range of GIS-rules adapting the method from Kidd et al. (2015) and simplified "categorical" parameter ranges. To quantify land suitability for a given environment, the model translates the "biophysical attributes" into "suitability indexes" through crop-specific "suitability rules". For example, suitable growing conditions might occur between temperature ranges of 5 to 25°C for a given crop, with an optimum within a narrower range (e.g. 15 and 20°C). Suitability classes (4 classes were defined, they are well suited, suitable, marginally suited, and unsuitable) for different attribute-crop combinations can be estimated based on such suitability rules. The overall suitability index of a crop at a specific location takes value from the worst index (limiting factor) out of all the attributes index at that location. Suitability rules were either generated from the literature and through consultation with crop-specific experts. Each crop went through one or more iterations where experts would evaluate the resulting national map from current rules, identify areas where suitability was not sensible and suggest improvements to the rules to obtain expected spatial patterns.
The suitability rules are simplifications of biophysically sound principles that operate at a much lower scale of organisation (e.g. crop and plant physiological responses to the environment). Such simplification is necessary, given that suitability assessments are performed at the landscape level.
Yield ranges for each suitability class were estimated by crop experts. The upper range of the well-suited class is based on the maximum "field" yields observed in New Zealand. Upper and lower bounds of national average crop yields are used for the suitable class range. Yield ranges in the marginally suited class are those limited by the environmental conditions with varying impact from year to year. Environments where yields are predicted to be zero or crops are considered uneconomic to harvest are classed as unsuitable.
References:
Kidd D, Webb M, Malone B, Minasny B, McBratney A. 2015. Digital soil assessment of agricultural suitability, versatility and capital in Tasmania, Australia. Geoderma Regional. 6: 7-21
Thomas S, Ausseil AG, Guo J, Herzig A, Khaembah EN, Palmer D, Renwick A, Teixeira E, Van der Weerden A, Wakelin S 2021. Evaluation of profitability and future potential for low emission productive uses of land that is currently used for livestock SLMACC Project 405422. MPI Technical Paper No:2021/13 Ministry for Primary Industries
Fitness for purpose / limitations
This table indicates whether the dataset is suitable for different types of questions at different scales.
Note: Users should carefully consider their purpose as this dataset may not be suitable.
|
Operational
| Absolute
| Relative
| Screening/scoping
|
| Block/farm |
No | No | No | Maybe |
| Multi-farms(5+) |
No | No | Maybe | Yes |
| Catchment |
No | Maybe | Maybe | Yes |
| National/regional |
No | Yes | Yes | Yes |
Caveat(s) |
Intended for national/regional use so limited accuracy especially at finer scales |
