Description
Douglas fir site suitability for afforestation, including:
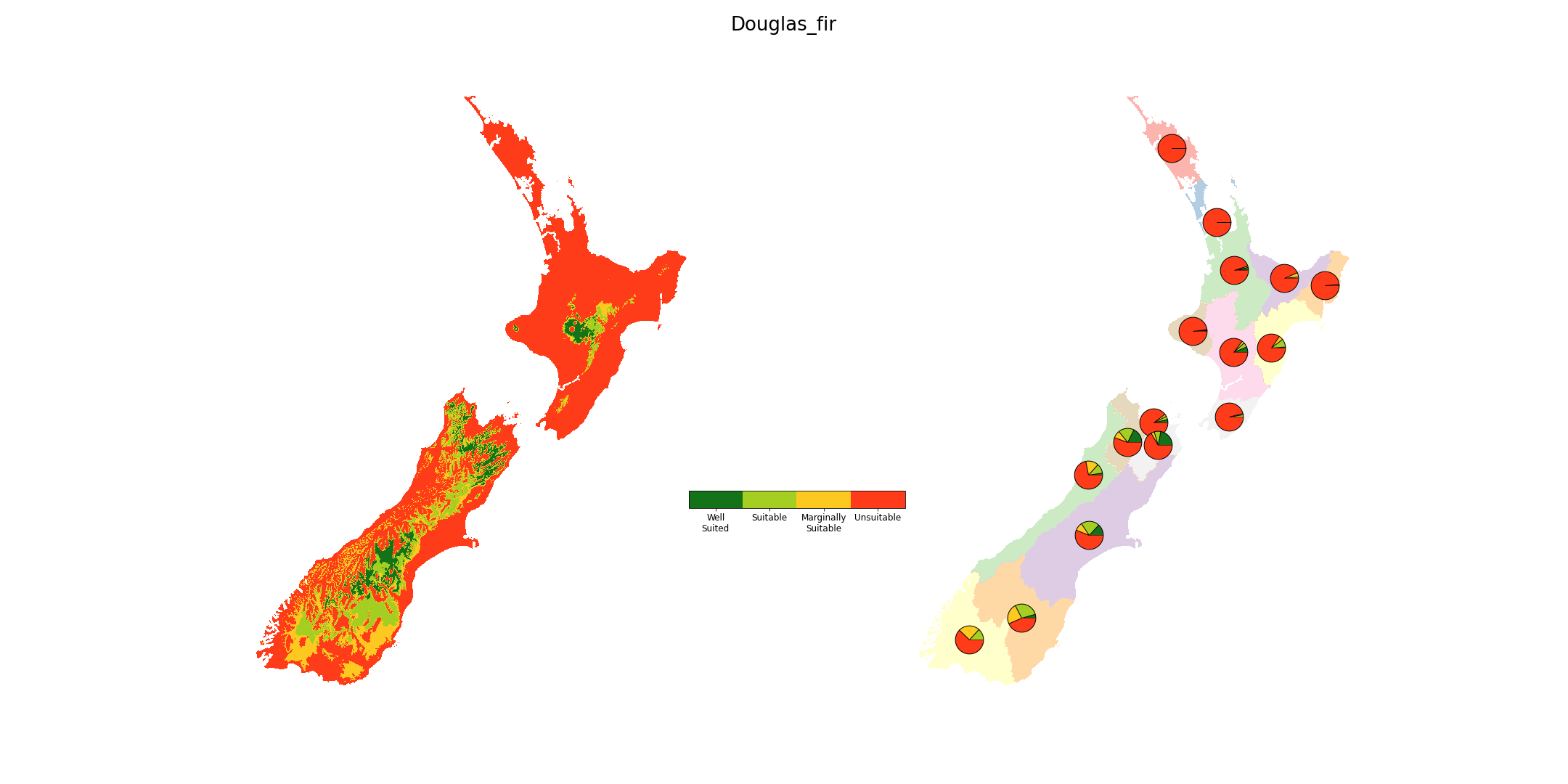
map of suitability categories (1 - Well suited, 2 - Suitable, 3 - Marginally suited, 4 - Unsuitable)
resampled map of suitability categories (1 - Well suited, 2 - Suitable, 3 - Marginally suited, 4 - Unsuitable)
rules used to generate the suitability maps
regional areas for the suitability categories
Date: November 2023 Version: v2
Owner: MPI
Contact: David Palmer, Scion
Link to report / paper
General approach:
Thomas S, Teixeira E, Ausseil A-G, Grealish G, Guo J, Velarde SJ, Palmer D, Renwick A, Van Der Weerden T. June 2018. The Sustainable Land Management and Climate Change (SLMACC) research programme: report for Phase 2 description of land suitability assessment methodology. A Plant & Food Research report prepared for: Ministry for Primary Industries. Milestone No. 74660. Contract No. 34828. Job code: P/443064/01. SPTS No. 16415
Kidd D, Webb M, Malone B, Minasny B, McBratney A. 2015. Digital soil assessment of agricultural suitability, versatility and capital in Tasmania, Australia. Geoderma Regional. 6: 7-21
Our Environment
You can view the data in this dataset on a map-based web app here:
Douglas Fir Suitability Categories
Preview Image
Dataset attributes
| Spatial extent |
New Zealand |
|---|
| Spatial resolution |
500 m pixel size, NIWA VCSN 5 km climate grid and FSL polygons |
|---|
| Temporal extent |
Based on historic/current climate |
|---|
| Temporal resolution |
N/A |
|---|
| Evaluation method (Validation) |
None |
|---|
| Evaluation result (Numeric) |
N/A |
|---|
| Evaluation result (Categorical) |
N/A |
|---|
| Uncertainty method |
None |
|---|
| Uncertainty data format (Numeric) |
None |
|---|
| Uncertainty data format (Categorical) |
Fuzzy membership
Reliability/Confidence rating |
|---|
Methodology
Forestry site suitability defined based on ranges in volume productivity, mean annual temperature, maximum October temperature, October frosts, February water deficits, and wind exposure. Python scripts and ArcGIS python libraries were used to calculate the fuzzy memberships from spatial layers using the Spatial Analyst tool fuzzy function “LINEAR” using the minimum and maximum values. For each factor, values were converted to a range between 0 (unsuitable) to 1 (optimal), then classified into four classes (WS - well suited; S - suitable; MS - marginally suited; U - unsuitable).
The overall suitability index of a crop at a specific location takes value from the worst index (limiting factor) out of all the attributes index at that location. Suitability rules were generated from the literature and through consultation with experts.
Fitness for purpose / limitations
This table indicates whether the dataset is suitable for different types of questions at different scales.
Note: Users should carefully consider their purpose as this dataset may not be suitable.
|
Operational
| Absolute
| Relative
| Screening/scoping
|
| Block/farm |
No | No | Maybe | Maybe |
| Multi-farms(5+) |
No | No | Maybe | Yes |
| Catchment |
No | Maybe | Yes | Yes |
| National/regional |
No | Maybe | Yes | Yes |
Caveat(s) |
Suitability rules are simplifications of biophysically sound principles that operate at a much lower scale of organisation (e.g. tree physiological responses to the environment). Productivity as assessed by spatial productivity index (itself based on environmental variables) is used as a surrogate for detailed factors. Such simplification is necessary, given that suitability assessments are performed at the landscape level. |
